Milk FAQS
British Universities and Colleges Sport | Privacy Policy | Cookies Policy
DO I NEED PROTEIN SHAKES TO GET ENOUGH PROTEIN IN MY DIET WHEN WORKING OUT?
Protein shakes are often popular with people who regularly work out, but milk makes a great and often cheaper alternative. The protein in milk naturally packaged together with heaps of other nutrients that the body is able to easily use. Milk isn't just a drink; it's a wholesome, well-rounded choice that can meet your nutritional needs without the added sugars or artificial ingredients often found in some protein shakes.
IS MILK BAD FOR MY SKIN?
While some studies suggest a potential link between dairy consumption and acne for some individuals, the relationship is complex and varies from person to person. Many people can consume dairy without experiencing adverse effects on their skin. Factors such as genetics, overall diet, and lifestyle also influence skin conditions. Additionally, dairy products like yogurt may contain probiotics that could have positive effects on skin health by promoting a balanced gut microbiome.
CAN YOU HYDRATE WITH MILK?
Staying hydrated is important, especially after exercise, as sweating causes the loss of both water and electrolytes like sodium and potassium. Even a small amount of dehydration - around 2% of body weight lost through sweat - can affect your concentration, decision-making, and reaction times.Milk is made up of around 88% water, so it can contribute to keeping you hydrated. Water is essential for maintaining normal body functions, such as helping your body stay cool and focused during and after exercise. As well as its high-water content, milk also contains important electrolytes like potassium and sodium, which help keep your body's fluid levels balanced.
WHEN IT IS BEST TO DRINK MILK?
Milk can be enjoyed at various times throughout the day depending on your needs. After exercise, milk can be beneficial because it provides high-quality protein, which supports muscle recovery contributing to the maintenance and growth of muscle mass. While milk does contain some carbohydrates, it’s typically combined with other foods to meet the recommended carbohydrate intake for recovery after intensive or prolonged exercise.In addition, milk is rich in essential nutrients like calcium and phosphorus, which contribute to the maintenance of normal bones and overall bone health. Whether as part of a post-exercise snack or integrated into meals throughout the day, milk can be a nutritious option.
DO I NEED TO CUT DOWN ON MILK BECAUSE IT CONTAINS SUGAR?
Plain milk doesn't contain any added sugars. The sugar it does contain (lactose) occurs naturally. The NHS agrees there is no need to avoid or limit the type of sugar found naturally in milk as it’s not harmful to health. Most flavoured milks do contain variable amounts of added sugar but still provide a rich package of beneficial nutrients which includes vitamins and minerals.
HOW DOES DAIRY MILK COMPARE TO PLANT ALTERNATIVES?
Oat drink is the latest player in the non-dairy alternative world, and is a popular choice when served up as an oat milk latte. While oat milk’s consistency may be similar to that of dairy milk,it’s important to know that it’s not a one-for-one swap. One of the biggest and most important differences is that dairy milk has three times the levels of protein as an oat drink. Protein is important to consider when choosing foods and beverages, as it helps build and maintain muscle.
Another difference is the vitamin and mineral content. Dairy milk naturally contains 7 vitamins and minerals, oat drinks do not naturally contain these nutrients in significant amounts and therefore have to be fortified with vitamins during manufacturing. Some varieties of oat drinks have up to ten ingredients, including added salt, sugar and rapeseed or sunflower oil, acidity regulators and stabilisers (such as Gellan Gum). That’s why it’s always important to read and compare nutrition labels and ingredient lists to make a well-informed choice.
I CAN'T DRINK MILK BECAUSE I AM LACTOSE INTOLERANT?
If you’re lactose intolerant, you can still enjoy certain dairy products and alternatives. Lactose-free milk is available and is treated to break down lactose, making it easier to digest while providing the same nutrients as regular milk.
Yogurt is another option to consider. Many people with lactose intolerance find that yogurt is easier to digest because the fermentation process reduces the lactose content. Look for yogurt that contains live cultures and choose lactose-free varieties if needed.
Plant-based drink, such as almond, soya, or oat drinks, are also suitable lactose free option. Always check the labels and choose ones that are fortified with calcium and other vitamins and minerals including Vitamin B12 and iodine.
IS IT GOOD TO DRINK MILK EVERY DAY?
Yes - lots of people in the UK drink milk daily, whether it’s in tea, coffee, cereal, or as a drink on its own. Milk is a natural source of important nutrients like calcium, protein, iodine, and vitamins B2 and B12.
There’s no set amount of milk you have to drink, but it’s a good idea to aim for 3 three portions of dairy each day, as part of a healthy balanced diet. A portion might include:
-
200ml of milk
-
A small pot of yogurt (about 125g)
-
A matchbox-sized piece of cheese (30g)
WHICH MILK IS BEST FOR BONES?
Whole/semi-skimmed/skimmed milk is a good source of calcium, which is needed for the maintenance of normal bones and teeth - especially important for children, teenagers, and older adults.
Adults need around 700mg of calcium per day. A 200ml glass of semi-skimmed milk provides 240mg calcium. If you buy a plant-based alternative, ensure it’s fortified with both calcium and vitamin D.
SHOULD ADULTS DRINK MILK?
Absolutely. The NHS recommends including some dairy or dairy alternatives every day. These provide important nutrients such as protein, calcium, iodine, and vitamin B12. If you choose dairy alternatives, make sure they are fortified with calcium.
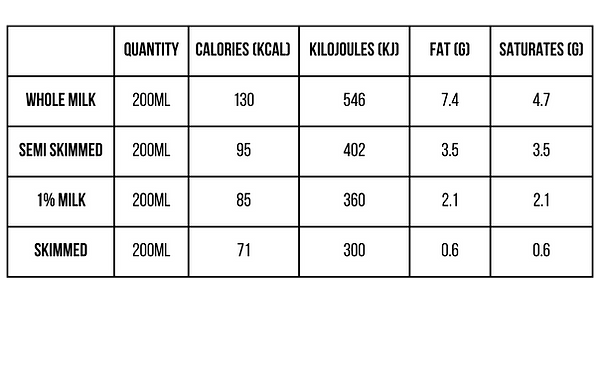
It’s also a good idea to choose lower-fat and lower-sugar options where possible. This includes semi-skimmed, 1% fat, or skimmed milk, low-fat natural yogurt, and reduced-fat cheese. Choose the type of milk that best meets your lifestyle and dietary needs.
DOES HEATING MILK MAKE A DIFFERENCE?
Heating milk can make a difference, but it depends on how much and how often it’s heated.
Gently warming milk (like in tea or porridge) doesn’t significantly affect its nutritional value. However, repeatedly boiling or overheating milk at high temperatures may slightly reduce heat-sensitive vitamins like vitamin B12. For most everyday uses, like cooking or hot drinks, heating milk is absolutely fine and won’t impact its main nutrients like calcium or protein.
IS MILK FATTENING?
Milk is not 'fattening' in itself - it depends how much you drink and what type you choose. Milk is a nutrient-dense drink, meaning it provides several important nutrients in relatively few calories.
-
Whole milk - around 66 kcal per 100ml
-
Semi-skimmed - 50 kcal per 100ml
-
Skimmed - 35 kcal per 100ml
If you're trying to reduce saturated fat or manage your weight, semi-skimmed or skimmed milk may be a better choice. Both options can be part of a healthy, balanced diet.
CAN I FREEZE MILK SAFELY?
Yes - you can freeze milk (within its use-by date), defrost it in the fridge, and use within a couple of days. But don’t freeze milk in glass bottles as they may crack.
WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN THE TYPES OF MILK?
All varieties of milk, including whole, semi-skimmed, 1% fat and skimmed, contain similar amounts of protein, and most vitamins and minerals. It’s the fat content that is different. The exception is vitamin A. This nutrient is removed with the fat so lower fat milks contain less.